Expectations from the Maintenance Manager
a. Work Instructions
As a maintenance manager, it is crucial to provide clear and documented work instructions for maintenance technicians. Maintenance work instructions can be defined as written guidelines that specify how a maintenance task should be performed and outline the expected quality standards for the work order. The reasons for having work instructions include:
- Managing and Limiting Human Error: Clearly defined instructions help reduce mistakes by providing precise guidelines.
- Reducing Variability in Task Performance: Standardizing procedures ensures consistent performance across tasks.
- Ensuring Adherence to Safety Procedures: Detailed instructions promote safety by outlining necessary precautions.
Maintenance work instructions are living documents subject to continuous improvement as we strive to find the most efficient and safest ways to perform tasks. They are typically drafted from OEM manuals combined with practical experience in equipment management. While OEM manuals often specify tasks to be performed at specific intervals, they usually lack detailed “how-to” procedures. Although many OEM manuals provide technical drawings of machine assemblies and subassemblies, these drawings may not be sufficient for technicians who need detailed, task-specific work instructions.
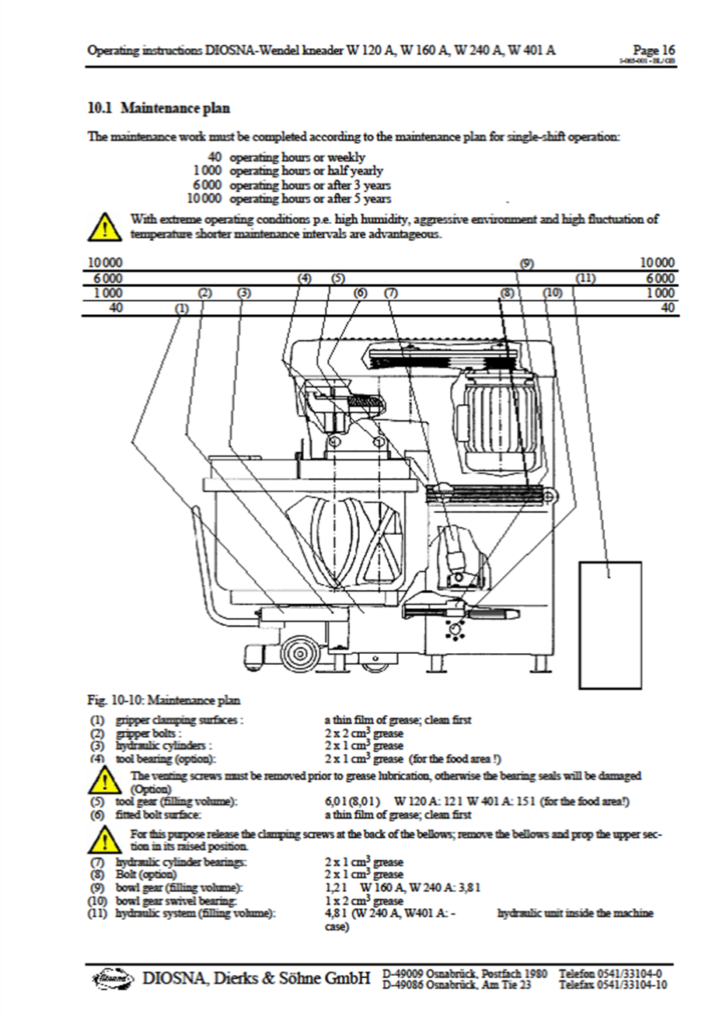
For example, the maintenance plan for a mixing machine by DISONA includes all necessary requirements, but it is the maintenance manager’s responsibility to extract this information and create concise, easy-to-understand work instructions. These instructions should be integrated into a computerized maintenance management system (CMMS) if available. Work instructions should be developed with the end-user (technicians) in mind and must include the following key elements:
- The Equipment: Clearly identify the equipment involved.
- The Maintenance Task: Describe the specific task to be performed.
- Acceptable Limits: Specify acceptable tolerances or conditions.
- Safety Instructions: Provide necessary safety precautions.
- Follow-Up Actions: Outline any subsequent steps or checks.
The figure below details the monthly preventive maintenance procedures for the mixer.

b. Training of Technicians
In addition to providing detailed work instructions, it is essential to conduct on-site training for technicians. This training ensures that technicians fully understand the working principles of the machine and can execute maintenance tasks as specified in the work instructions. Training bridges the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, ensuring that maintenance functions are performed correctly and efficiently.




What are your thoughts?